Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1
Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1
Bezitramide is an opioid analgesic. Bezitramide itself is a prodrug which is readily hydrolyzed in the gastrointestinal tract to its active metabolite, despropionyl-bezitramide.[2] Bezitramide was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1961.[3][4][5] It is most commonly marketed under the trade name Burgodin.
The drug was pulled from the shelves in the Netherlands in 2004 after fatal overdose cases, including one where a five-year-old child took one tablet from his mother’s purse, ate it, and promptly died.[6]
Bezitramide is regulated much the same as morphine in all known jurisdictions and is a Schedule II substance under the United States’ Controlled Substances Act of 1970, with an ACSCN of 9800 and zero annual manufacturing quota.[7] However, as of May 2021, it has never been marketed in the United States.
Bezitramide cas: 15301-48-1
| CBNumber: | CB5901881 |
| Chemical Name: | bezitramide |
| Molecular Formula: | C31H32N4O2 |
| Formula Weight: | 492.61 |
| CAS No.: | 15301-48-1 |
Noteworthy Information: Bezitramide was once prescribed for very painful conditions, but it was pulled from circulation because of the high danger of overdose, according to research. Urea Formaldehyde Methylene powder
– A Bezitramide (CAS 15301-48-1) probably targets opioid receptors via its metabolite despropionyl-bezitramide. Buy Tapentadol Hydrochloride CAS-175591-09-0
Some areas withdrew from the market by 2004 due to serious safety concerns, even though the product had not yet received clearance from the United States. The significant danger of overdose, as shown by fatal instances, is a source of controversy that affects both its regulatory position and its therapeutic usage.
Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1
Bezitramide has been around since the 1960s and is well-known for its effectiveness in treating severe chronic pain. It is a synthetic opioid analgesic. Nevertheless, it has a checkered past characterized by serious safety concerns, which caused it to be pulled from several markets in 2004 because of deadly overdoses. Those curious about its chemical characteristics, health advantages, and current restricted use may find a comprehensive summary in this page.
Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1, Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1
Overview of Chemicals and Their Use
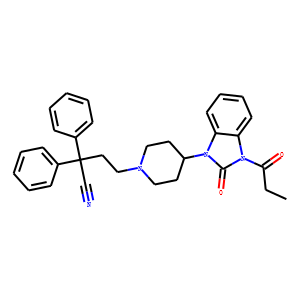
C31H32N4O2 is the molecular formula and 492.611 g/mol is the formula weight of bezitramide, whose chemical name is 4-[4-(2-oxo-3-propanoyl-benzoimidazol-1-yl)-1-piperidyl]-2,2-diphenyl-butanenitrile. Its opioid properties make it a restricted drug; its CAS number is 15301-48-1. Safety issues have limited its usage, although it was once marketed as Burgodin for pain management. Buy Bezitramide Cas 15301-48-1
Present Situation Regarding Safety
A youngster died from only one pill of Bezitramide, and other studies have shown that the drug posed a significant risk of deadly overdoses, prompting its withdrawal. There are still worries regarding its safety profile, hence it is not currently available for sale and is classified as a Schedule II chemical in the US.
Note for Survey: Bezitramide Comprehensive Analysis
Greetings and Background Information
Bezitramide, a synthetic opioid analgesic with the CAS number 15301-48-1, was created by Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1961 and sold under the brand name Burgodin. Its creation as a long-acting analgesic for the treatment of severe chronic pain reflects the time’s emphasis on creating powerful opioids for medicinal purposes. Unfortunately, its therapeutic use was cut short when it was removed from some markets in 2004 due to fatal overdose occurrences, one of which included a five-year-old kid. A Schedule II banned drug under the banned Substances Act of 1970, it has never been sold in the United States as of April 15, 2025. Its zero yearly production quota highlights its significant misuse potential and safety issues.
Chemical Make-Up and Characteristics
Four-[4-(2-oxo-3-propanoyl-benzoimidazol-1-yl)-1-piperidyl] is the chemical name of bezitramide. The chemical formula and formula weight of -2,2-diphenyl-butanenitrile are C31H32N4O2 and 492.611 g/mol, respectively. The nitrile group, piperidine ring, and benzimidazolone ring system make it very potent and lipophilic. It has a melting point range of 150-200°C, is mostly insoluble in water but more soluble in organic solvents, and is a crystalline powder that may be white or off-white in color. Although it may deteriorate in very hot or bright environments, it is stable under typical use.
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-(2-oxo-3-propanoyl-benzoimidazol-1-yl)-1-piperidyl]-2,2-diphenyl-butanenitrile |
| Molecular Formula | C31H32N4O2 |
| Formula Weight | 492.611 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 15301-48-1 |
| Physical State | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water, soluble in organic solvents |
| Stability | Stable under normal conditions |
A Look at Popular Search Terms
Some of the most common online searches for Bezitramide include: – Bezitramide, Burgodin, opioid analgesic, despropionyl-bezitramide, Janssen Pharmaceutica, narcotic, pharmaceutical, drug withdrawal, fatal overdose, controlled substance, analgesic, opioid, pain management, scheduled II substance, pharmaceutical company.
These terms indicate that people are curious in its chemical composition, medicinal applications, and regulatory background, especially with regard to its withdrawal and safety concerns.
Market Dynamics
Fentanyl, a powerful synthetic opioid with a fast onset, is one of many opioids used to treat severe pain; bezitramide is in competition with it.
– Another analgesic was developed around this time, dextropromoramide.
– Methadone, an opioid that alleviates pain and addiction with a lengthy half-life.
– The most common opioid for extreme pain is morphine.
Although they are structurally and therapeutically similar, the opioid receptor agonism, efficacy, and duration of action of these drugs are distinct; notably, bezitramide has a long-acting profile.
Positive Health Outcomes and Clinical Effectiveness
Severe chronic pain, especially that which occurs after lumbar disc surgery or other operations, was well treated with bezitramide. It had a longer duration (up to 24 hours) and greater efficacy than dextromoramide (5 mg orally) in male patients, according to clinical studies such as a 1970 research by Knape. With little respiratory depression and almost no adverse effects, it showed promise for chronic pain treatment in a 1971 trial included 99 patients.
Possible Consequences and Dangers
Bezitramide is an excellent mood stabilizer, but it carries the potential of deadly overdosing; one youngster died after taking only one pill. In addition to the usual opioid side effects, there are additional consequences such as respiratory depression, drowsiness, vertigo, constipation, and dependency. Its safety was questioned because to its enormous potency (20 times that of methadone) and its limited therapeutic window.
How It Work
The prodrug bezitramide is hydrolyzed in the digestive system to despropionyl-bezitramide, a powerful agonist for the ν-opioid receptor. In line with its usage for chronic pain, this activation decreases pain perception via descending inhibitory pathways. The effect lasts for a long time because of the metabolite’s pharmacokinetics.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Record
The 2004 removal in the Netherlands was due to safety concerns; in the US, it is classified as Schedule II (ACSCN 9800, nil quota), indicating a significant potential for misuse. Pharmacokinetic data showing a Cmax of 5.4 ng/ml, lag time of 0.5-1.0 hours, and half-life of 11-24 hours, suggesting variable absorption and excretion, together with its market removal and lack of FDA clearance, highlight persistent concerns.
Dangers and Safety Measures
Fatal overdose danger, respiratory depression, drowsiness, and gastrointestinal problems are important adverse effects. Avoid usage in youngsters, anyone with respiratory issues, or those taking MAOIs at the same time as a precaution; patients should be closely monitored for withdrawal symptoms and dependency.
Timing and Execution
The 5 mg oral dosage was tested in studies to have an onset time of around 1 hour, a peak time of 2.5–3.5 hours, and a duration of up to 24 hours. Dosage must be carefully monitored to prevent toxicity, since pharmacokinetic studies reveal biliary excretion of a large amount and less than 0.3% urine excretion.
Not recommended
The dangers associated with the opioid class need care in patients with hypersensitivity, severe respiratory depression, acute asthma, paralytic ileus, usage in children, and impaired liver or kidney function.
Research Studies and Archival Information
Efficacy was shown while overdose hazards were highlighted in trials conducted in the 1970s that contrasted Bezitramide with dextromoramide, such as Knape’s investigations. Results from pharmacokinetic investigations in seven volunteers corroborated its long-acting nature and varied duration, lending credence to its use in chronic pain management but also highlighting some safety concerns.
In summary
The tale of bezitramide shows how opioid research and development must strike a balance between safety and effectiveness. Although it is effective, the fact that it may be dangerously overdosed makes thorough safety evaluations all the more important. There has been no therapeutic usage of this banned chemical since April 15, 2025, and it continues to serve as a cautionary tale in the field of pharmaceutical research.
Others also inquire
1. How is Bezitramide put to use?
Used to provide long-lasting relief from severe chronic pain, especially after surgery.
2. What caused the withdrawal of Bezitramide?
Emphasizing the dangers, withdrawal occurred as a result of lethal overdoses, one of which was a toddler.
3. Is the medication Bezitramide still sold?
Restricted availability; not sold in the US; removed in some places (e.g., the Netherlands).
4. Could you please explain side effects?
Risk of deadly overdose, sedation, constipation, depression of the respiratory system, and dependency are all part of it.
5. What’s the deal?
The prostaglandin was changed into despropionyl-bezitramide, which alleviated pain by acting as an agonist for the μ-opioid receptor.
bezitramide
For research use only. Not for therapeutic Use.
- CAT Number: M087886
- CAS Number: 15301-48-1
- Molecular Formula: C31H32N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 492.623
- Purity: ≥95%
| CAS Number | 15301-48-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C31H32N4O2 |
| Purity | ≥95% |
| Storage | Store at -20C |
| IUPAC Name | 4-[4-(2-oxo-3-propanoylbenzimidazol-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl]-2,2-diphenylbutanenitrile |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C31H32N4O2/c1-2-29(36)35-28-16-10-9-15-27(28)34(30(35)37)26-17-20-33(21-18-26)22-19-31(23-32,24-11-5-3-6-12-24)25-13-7-4-8-14-25/h3-16,26H,2,17-22H2,1H3 |
| InChIKey | FLKWNFFCSSJANB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC(=O)N1C2=CC=CC=C2N(C1=O)C3CCN(CC3)CCC(C#N)(C4=CC=CC=C4)C5=CC=CC=C5 |
| Chemistry Calculators | Dilution Calculator In vivo Formulation Calculator Molarity Calculator Molecular Weight Calculator Reconstitution Calculator |
bezitramide
- Product Name
- bezitramide
- CAS No.
- 15301-48-1
- Chemical Name
- bezitramide
- Synonyms
- R 4845;bezitramide;FLKWNFFCSSJANB-UHFFFAOYSA-N;1-[1-(3-Cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-piperidinyl]-1,3-dihydro-3-(1-oxopropyl)-2H-benzimidazol-2-one;1-Piperidinebutanenitrile, 4-[2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-3-(1-oxopropyl)-1H-benzimidazol-1-yl]-α,α-diphenyl-
- CBNumber
- CB5901881
- Molecular Formula
- C31H32N4O2
- Formula Weight
- 492.61
- MOL File
- 15301-48-1.mol
bezitramide Property
- Melting point:
- 145-149°; mp 124.5-126°
- Boiling point:
- 586.35°C (rough estimate)
- Density
- 1.1470 (rough estimate)
- refractive index
- 1.6000 (estimate)
- solubility
- DMSO: Soluble: = 10 mg/ml
- pka
- 8.21±0.10(Predicted)
- color
- White, crystalline powder
Safety
- Toxicity
- LD50 orally in mice, rats: 2101, 141 mg/kg (Janssen)
bezitramide Chemical Properties,Usage,Production
Originator
Bezitramide,ZYF Pharm Chemical
Uses
Bezitramide is a narcotic analgesic agonist with modified pipiridine N-substituents whose binding affinity to the ORL1 and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors is of research interest.
Definition
ChEBI: Bezitramide is a nitrile.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 6.9 parts 4-bromo-2,2-diphenylbutyronitrile, 5 parts 4-(2-oxo-1- benzimidazolinyl)piperidine, 7.3 parts sodium carbonate, a few crystals of potassium iodide in 160 parts 4-methyl-2-pentanone is stirred and refluxed for 12 hours. After cooling the reaction mixture, 100 parts water is added. The aqueous layer is separated and extracted with 4-methyl-2-pentanone. The combined organic layer are dried over MgSO4 and evaporated. The oily residue is dissolved in a mixture of 24 parts diisopropylether and 24 parts isopropanol. After cooling overnight to -20°C, 5.3 parts product are obtained. This crop is boiled in 72 parts 4-methyl-2-pentanone and cooled to 0°C, yielding 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-(2-oxo-1-benzimidazolinyl) piperidine, melting point 225-226°C, as a grey-white amorphous powder.
A mixture of 5 parts 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-(2-oxo-1- benzimidazolinyl)piperidine, 7.5 parts propionic acid anhydride and 80 parts benzene is stirred and refluxed for 16 hours. After cooling, the reaction mixture is washed twice with 100 parts water. The aqueous layer is dried over potassium carbonate, filtered and evaporated. The residue is recrystallized from 60 parts of ether, yielding 4 parts crude 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)- 4-(2-oxo-3-propionyl-1-benzimidazolinyl)piperidine. This crop is recrystallized from 20 parts m-methyl-2-pentanone 4-ethyl-2-pentanone, yielding 1-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-(2-oxo-3-propionyl-1-benzimidazolinyl)piperidine with melting point: 124.5-126°C as a pale yellow amorphous powder.
Therapeutic Function
Narcotic analgesic, Antitussive
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Caution: Maybe habit forming. This is a controlled substance (opiate)listed in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21Part 1308.12 (1985). When heated to decomposition itemits toxic fumes of NOx and CN–.
bezitramide Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
bezitramide Suppliers
15301-48-1, bezitramideRelated Search:
- bezitramide
- 1-[1-(3-Cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)-4-piperidinyl]-1,3-dihydro-3-(1-oxopropyl)-2H-benzimidazol-2-one
- R 4845
- FLKWNFFCSSJANB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- 1-Piperidinebutanenitrile, 4-[2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-3-(1-oxopropyl)-1H-benzimidazol-1-yl]-α,α-diphenyl-
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Bezitramide has poor water solubility, thus administration is restricted to the oral route. Less than 0.3% of the dose was excreted unchanged in the urine. High concentrations in feces suggested incomplete absorption of biliary excretion. Experiments in rats demonstrated extensive (up to 70%) biliary excretion, and less than 3% urinary excretion. Metabolism / Metabolites Biological Half-Life |
|---|---|
| Additional Infomation |
Bezitramide is a nitrile.
Bezitramide is a DEA Schedule II controlled substance. Substances in the DEA Schedule II have a high potential for abuse which may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence. It is a Opiates substance. Bezitramide is a narcotic analgesic which was discovered in 1961, clinically tested around the 1970’s, and marketed under the name Burgodin. After cases of fatal overdose in the Netherlands in 2004 the drug was withdrawn from the market. Bezitramide has never been FDA approved and is currently a schedule II drug. Drug Indication Pharmacodynamics |
| Molecular Formula |
C31H32N4O2
|
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight |
492.61138
|
| Exact Mass |
492.252
|
| CAS # |
15301-48-1
|
| PubChem CID |
61791
|
| Appearance |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| Melting Point |
145-149 °C
|
| LogP |
5
|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
0
|
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4
|
| Rotatable Bond Count |
7
|
| Heavy Atom Count |
37
|
| Complexity |
827
|
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count |
0
|
| InChi Key |
FLKWNFFCSSJANB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C31H32N4O2/c1-2-29(36)35-28-16-10-9-15-27(28)34(30(35)37)26-17-20-33(21-18-26)22-19-31(23-32,24-11-5-3-6-12-24)25-13-7-4-8-14-25/h3-16,26H,2,17-22H2,1H3
|
| Chemical Name |
4-[4-(2-oxo-3-propanoylbenzimidazol-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl]-2,2-diphenylbutanenitrile
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations
(e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) View MoreInjection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] Oral Formulations
Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) View MoreOral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400
Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0300 mL | 10.1500 mL | 20.3000 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4060 mL | 2.0300 mL | 4.0600 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2030 mL | 1.0150 mL | 2.0300 mL |
*Note: Please select an appropriate solvent for the preparation of stock solution based on your experiment needs. For most products, DMSO can be used for preparing stock solutions (e.g. 5 mM, 10 mM, or 20 mM concentration); some products with high aqueous solubility may be dissolved in water directly. Solubility information is available at the above Solubility Data section. Once the stock solution is prepared, aliquot it to routine usage volumes and store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles.
Molarity Calculator allows you to calculate the mass, volume, and/or concentration required for a solution, as detailed below:
- Calculate the Mass of a compound required to prepare a solution of known volume and concentration
- Calculate the Volume of solution required to dissolve a compound of known mass to a desired concentration
- Calculate the Concentration of a solution resulting from a known mass of compound in a specific volume





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.